In the previous article, we talked about the commonly used design terms in “Research and Ideation” category. You can check the first article of this series here if you have missed out.
Here are the next set of design terms, those you will find useful to keep handy when you study foundation as well as deeper in this area.
User-Centered Design
This iterative design process aims at understanding the user perspective (their thoughts, beliefs, motivations, etc.) for creating highly accessible and usable products for them. Wide variety of design and research techniques are used in this procedure. Also, it involves a mix and match of generative ideas (rigorous brainstorming sessions) and investigative tools ( surveys and interviews ) for a deep understanding of the needs of the users.
Human-Computer Interaction
Human-computer interaction is a systematic study which aims at improvising the overall experience for smooth communication between humans and computers.
Interaction between human and computer should be as friendly as conversations between two humans. Specialized design process, emotional design, and human psychology are its three major integral parts.
Ultimate goals of Human Computer-Interaction are :
- Understanding the ways of improving user experience
- Understanding user behavior in order to determine as to how people can use technology
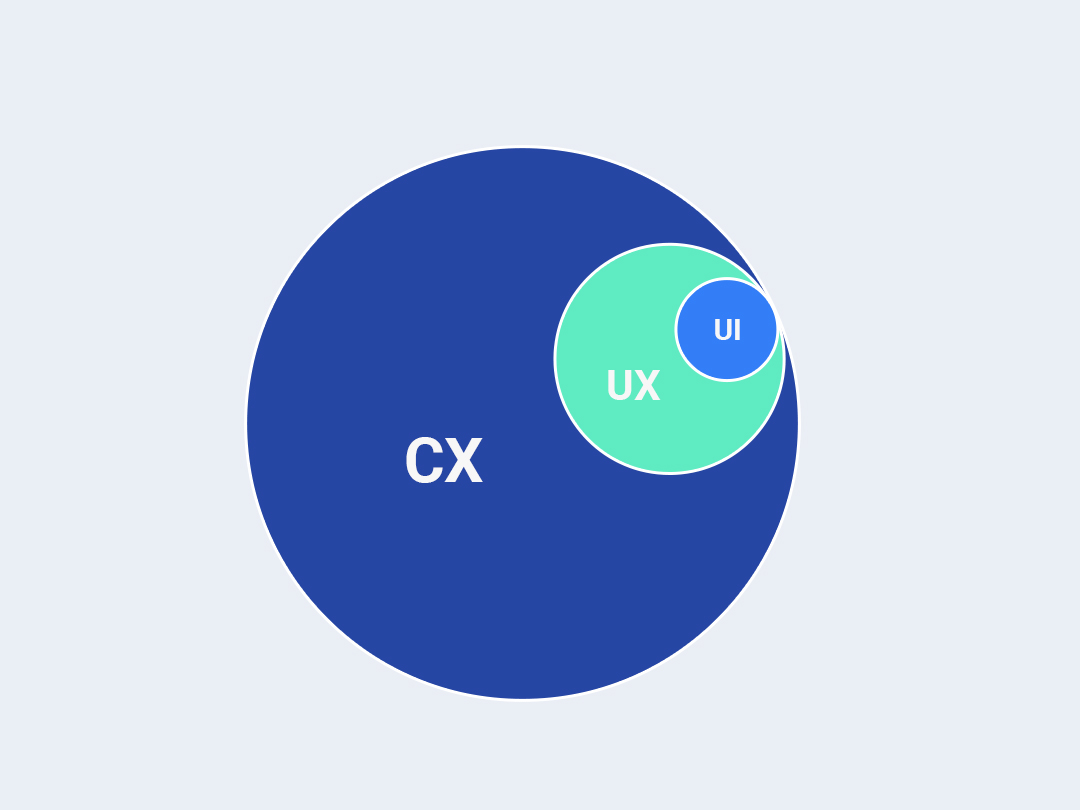
UX Design
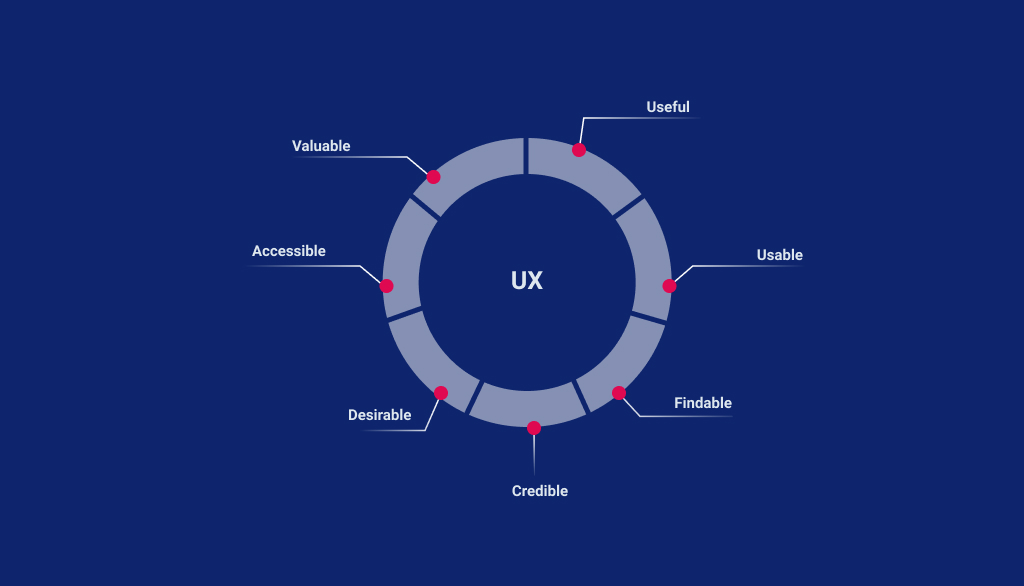
User Experience includes everything that contributes to physical & mental experiences of the user while using the product or service. It may include the user’s journey, information flow, content text, videos, images, graphics, interfaces, colors, interactions with the products/services. It is a step-by-step process which aims at creating meaningful & engaging products & platforms for the end users. User experience design follows a multidisciplinary approach that covers the entire process from branding, analysis, research, design, interaction, accessibility, usability, functional development & frequent upgradation.
We have discussed more in detail about UX Design, elements of UX design & different career options in our article which you can read here.
Lean UX
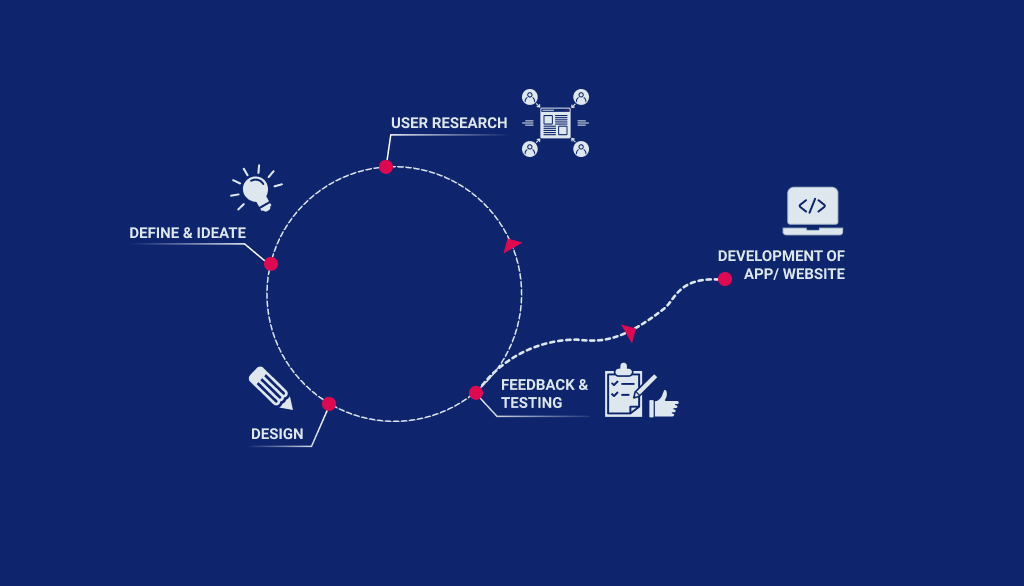
As an Agile development in software development, Lean UX is about creating the design in rapid way, mostly depending on assumptions, to get maximum feedback as early as possible. Unlike traditional or comprehensive UX Design process, Lean UX eliminates in depth activities to arrive at something tangible quick
Some of the major benefits of using this technique are :
- Cost Effectiveness: Don’t waste your resources in working on a product which isn’t needed in the market. You can easily test your hypothesis by validating every decision.
- Save your precious time: Due to its collaborative nature, getting rapid and quick solutions becomes easier.
- User-centric: Focus is on the user and their requirements at every stage of the designing process.
Responsive Design

It is a holistic approach which makes use of cascading style sheets, flexible layouts, and images to enhance user experience across all devices. Its ultimate purpose is to refine the appearance of the website according to the orientation and the screen size of the device which the user is using.
This technology is adept at adapting automatically according to user preferences and needs. This helps to get rid of a different design for every new gadget in the market.
Interaction Design
The process of interaction design takes into account like how users will interact and use the product or particular interface or even a particular piece of content. Five major dimensions in interaction design include words, visual representations, time, physical objects and behavior.
Wireframe

Wireframe refers to designing a website at a very nascent stage. A wireframe is used for laying out content and functionality on a page which takes into account the preferences and requirements of the users. Wireframes are used in the initial design process to set the basic structure of a page before visual design can be added. There are two phases in wireframing activity Low Fidelity & High Fidelity Wireframing.
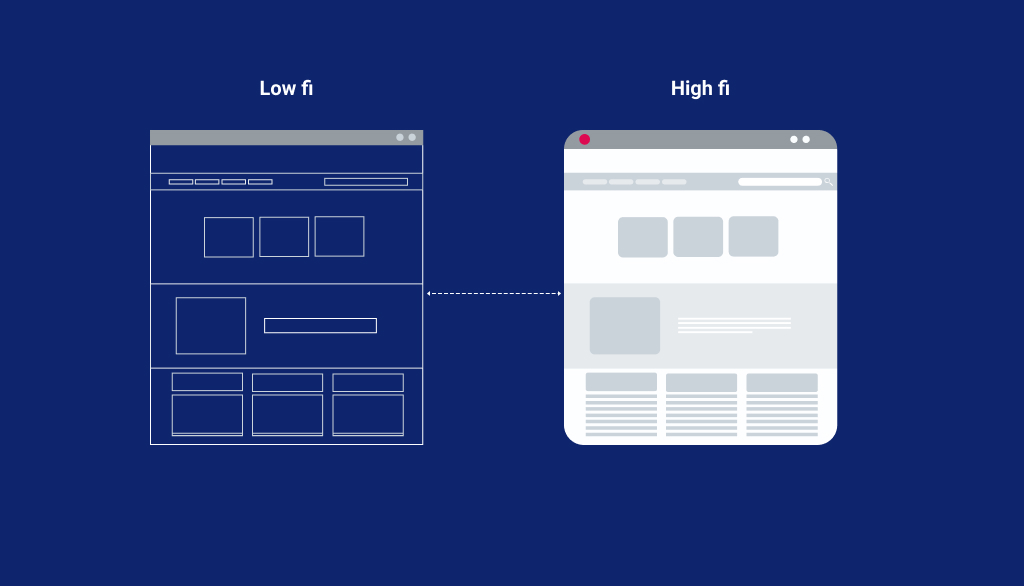
Low Fidelity Wireframes

Low Fidelity Wireframes are an easy and quick way to translate high-level design concepts into testable artifacts. The aspects of visual designing for the final product include basic visual hierarchy, shapes of elements and more. Typically they are in black white (or any two contrast colors)
High Fidelity Wireframes
High Fidelity Wireframes are more effective than low fidelity wireframes as they reveal what content & functions will go where and how, using guidelines of layout as well. Apart from that, high fidelity wireframes are refined and consist of various elements like images, graphics, color scheme, logo and more. They are created using digital tools and hence the process is more time consuming.
Prototype
A prototype is basically a primitive version of something that is iterated upon until it is a final product. It is a simple & easy version of the product or website. It helps to understand the simple workings of a product and its interaction with the user on creation of the final product. Prototype can have static interface (series) or in the form of clickable simulations of interfaces
UI (User Interface) Design

UI Design is a process of creating an interface between human (user), software and machine/hardware. This interface is actually a virtual (sometimes physical) layer where interaction between user, software and hardware takes place.
UI Design is a phase when designer converts the wireframe into final visual design with appropriate fonts, colors, graphics and, icons by focusing more on visual design aesthetics. UI design must follow some guidelines for usability like font sizes, usage of color shades, content hierarchy, consistency, accessibility guideline, etc.
Use Cases
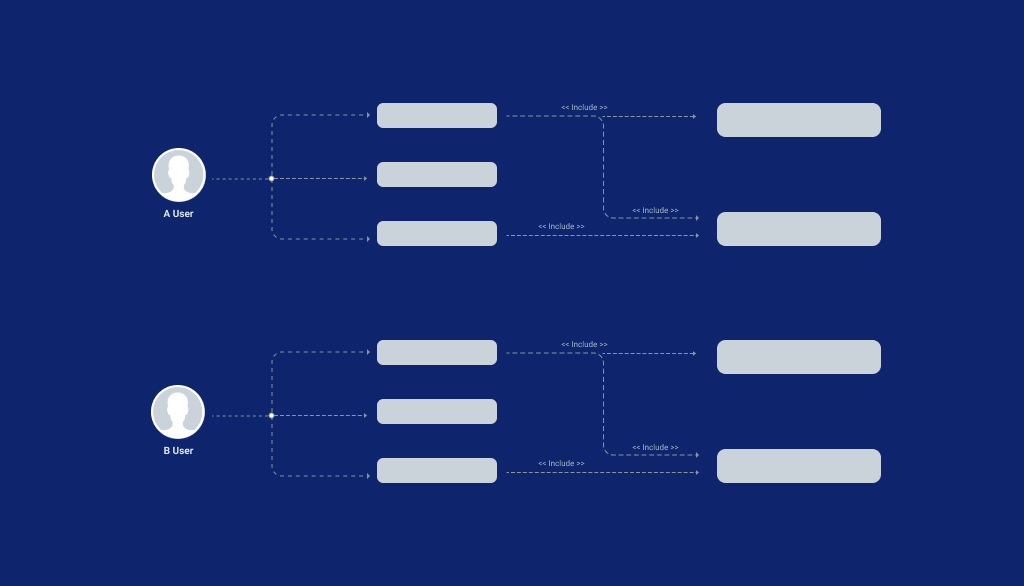
Use Case is a brief of how the system will respond to the user against the action the user is performing. Use cases take into account all the possibilities where different options or tasks with a combination of other possible options or tasks in the application/website. Use Cases are to be considered and recorded while planning & designing an application. Apart from that, use cases also provides a list of comprehensive goals as to how the system should behave in certain processes.
Affordance
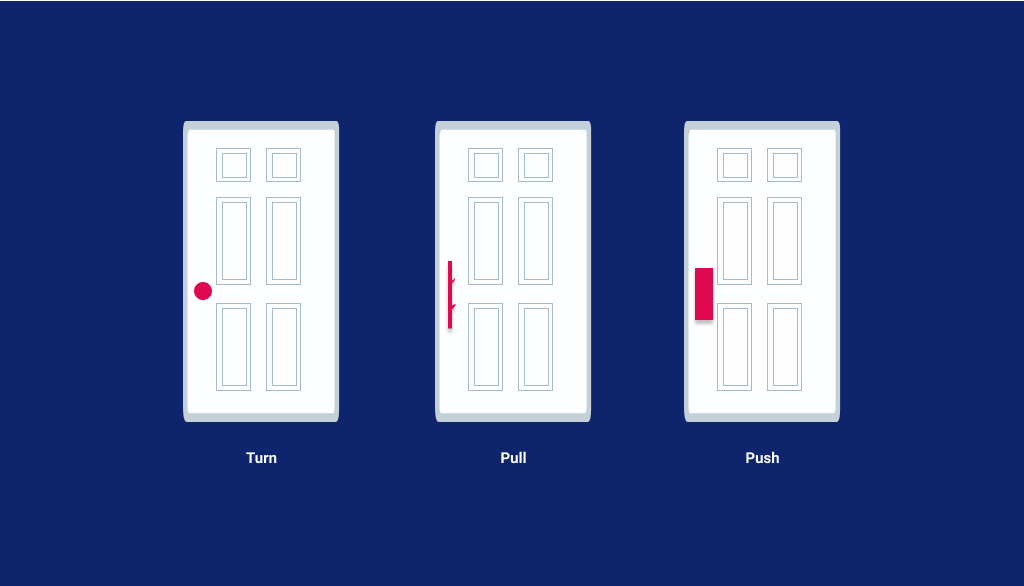
Affordances are nothing but visual clues in a design. They help the users to understand your UI efficiently and effectively. Improving the clarity of interface is vital to getting more visibility from the users.
For e.g. a door handle can indicate whether it can afford to push or pull.
Service Blueprints
Service blueprints are simple and clear diagrammatic representation of the services of a business as a whole. Their end goal is to understand the pain points of the customers and discover the internal shortcomings in their workings so as to improvise their working process. It aims at visualizing the organizational processes to optimize how a business can aim at delivering a great user experience.
Navigation Design

Navigation design is a discipline to design the ways for helping users to navigate through the platform (website or app or product or even physical space)
Navigation design plays an important role in creating a full-proof system that allows the users to interact and use the products in the most effective way. It is how your user can get from point A to point B or point C in an easy and hassle-free way.
Some of the advantages of a good navigation design are enhanced credibility and visibility of product, increased conversions due to more traffic, enhanced user experience and more.
MVP

Minimum Viable Product is the process of developing or designing a product with the least but its core features so that it can be quickly deployed for testing the market viability and acceptance amongst product’s potential customers.
Several benefits of carrying out MVP Process are understanding your customer preferences and needs, getting insights into whether the product is needed by users or not and checking the viability in the market by launching the product with minimal features.
I hope you enjoyed reading. Please feel free to share your comments and thought or any other terms if you wish to include in this list. Soon we will come up with the next part of this article with a few more interesting terms.